Project History
This is an assessment of the equipment and personnel loss in the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Several visualization tools including bar charts, geospatial maps, area charts, and box plots are used to show trends and patterns observed in the data.
On February 24th,2022 Russia launched a large-scale invasion of Ukraine. Here is a timeline of Ukraine’s fraught relationship with Moscow since it won independence in 1991 and the events that led to the current conflict.
-
1991: Shortly after the fall of the Soviet Union, Ukraine declares independence from Moscow.
-
2004: Pro-Russian candidate Viktor Yanukovich is declared president but allegations of vote-rigging trigger protests, known as the Orange Revolution, forcing a re-run of the vote. Pro-Western former prime minister, Viktor Yushchenko, is elected president.
-
2005: Yushchenko takes power with promises to lead Ukraine out of the Kremlin’s orbit, towards NATO and the EU.
-
2008: NATO promises Ukraine it will one day join the alliance.
-
2010: Yanukovich wins a presidential election.
-
2013: Yanukovich’s government suspends trade and association talks with the EU and opts to revive economic ties with Moscow, triggering months of mass rallies in Kyiv.
-
2014: Parliament votes to remove Yanukovich after bloodshed in the protests. Within days, armed men seize parliament in the Ukrainian region of Crimea and raise the Russian flag. Moscow later annexes the territory.
-
2017: An association agreement between Ukraine and the EU opens markets for free trade of goods and services, and visa-free travel to the EU for Ukrainians.
-
2019: Former comic actor Volodymyr Zelenskiy is elected president.
-
Jan. 2021: Zelenskiy appeals to U.S. President Joe Biden to let Ukraine join NATO. In February, his government freezes the assets of opposition leader Viktor Medvedchuk, the Kremlin’s most prominent ally in Ukraine.
-
Spring 2021: Russia begins massing troops near Ukraine’s borders in what it says are training exercises.
-
Nov. 2021: Satellite images taken by Maxar Technologies show ongoing buildup of Russian forces near Ukraine with estimates soon surpassing 100,000 troops deployed.
-
Dec. 17, 2021: Russia presents security demands including that NATO pull back troops and weapons from eastern Europe and bar Ukraine from ever joining.
-
Jan. 24, 2022: NATO puts forces on standby and reinforces eastern Europe with more ships and fighter jets.
-
Jan. 26, 2022: Washington responds to Russia’s security demands, repeating a commitment to NATO’s “open-door” policy while offering a “pragmatic evaluation” of Moscow’s concerns. Two days later Russia says its demands were not addressed.
-
Feb. 2022: Amid growing Western fears Russia could attack Ukraine, the United States says it will send 3,000 extra troops to NATO members Poland and Romania. Washington and allies say they will not send troops to Ukraine, but warn of severe economic sanctions if Russian President Vladimir Putin takes military action.
-
Feb. 21, 2022: In a TV address, Putin says Ukraine is an integral part of Russian history and has a puppet regime managed by foreign powers. Putin ordered what he called peacekeeping forces into two breakaway regions in eastern Ukraine, after recognizing them as independent.
-
Feb. 22, 2022: The U.S., Britain, and their allies sanction Russian parliament members, banks, and other assets in response to Putin’s troop order. Germany halts the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline project.
-
Feb. 23, 2022: Russian-backed separatist leaders ask Russia for help repelling aggression from the Ukrainian army.
-
Feb. 24, 2022: Putin authorizes “special military operations” in Ukraine. Russian forces begin missile and artillery attacks, striking major Ukrainian cities including Kyiv.
-
Feb. 26, 2022: Western allies announce new sanctions, including restrictions on Russia’s central bank and expelling key banks off the main global payments system.
Data Sources
The dataset used in this project was obtained from Kaggle. It contains details about equipment loss and death toll as the invasion continues; and is updated weekly along with this assessment. For an interactive dashboard tracking the changes in the dataset, click here. For the most recent version of this assessment, click here.
Programming Language Used:
- Python
Packages Used:
- Pandas
- Numpy
- Matplotlib
- Seaborn
- Plotly
- Folium
- Wordcloud
File Type:
- Jupyter Notebook
Research Questions Answered:
- On an interactive map, locate the country being invaded.
- How many Prisoners of War have been captured to date?
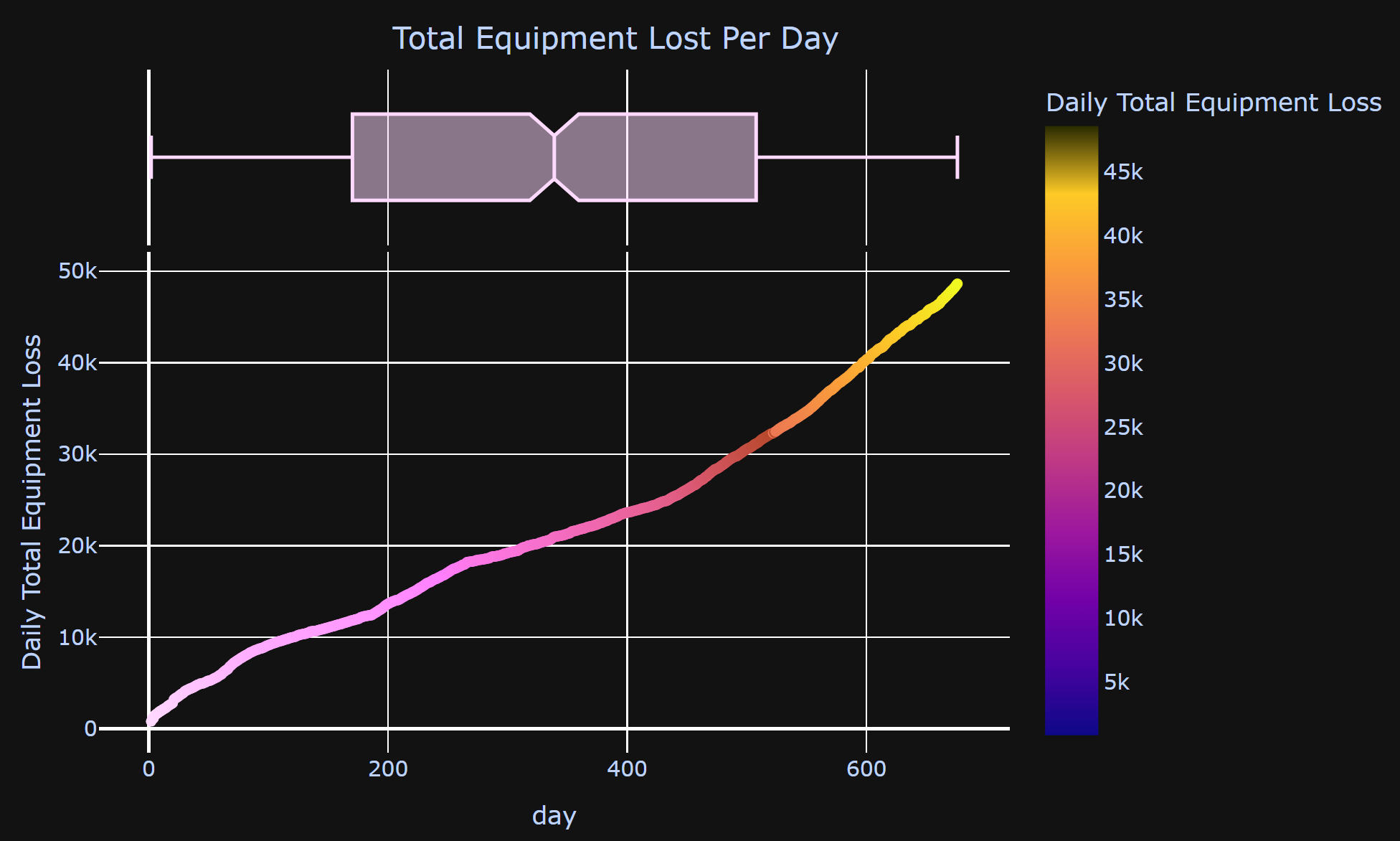
- What is the total count of equipment lost in the war?
- What is the correlation between Prisoners of War and equipment loss?
- What inferences can be made from the data and correlations within the data?
Sample Output